Technology
Transparency
Firewall-protected hosted GIS and Pix4D Cloud for project status, approvals, upload/download
Quality
Automated tabular & spatial QC at multiple stages of the project and manual QC checkpoints.
Agility
Automated deliverable creation customized to customer requirements.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS Web Map Example: Pipelines
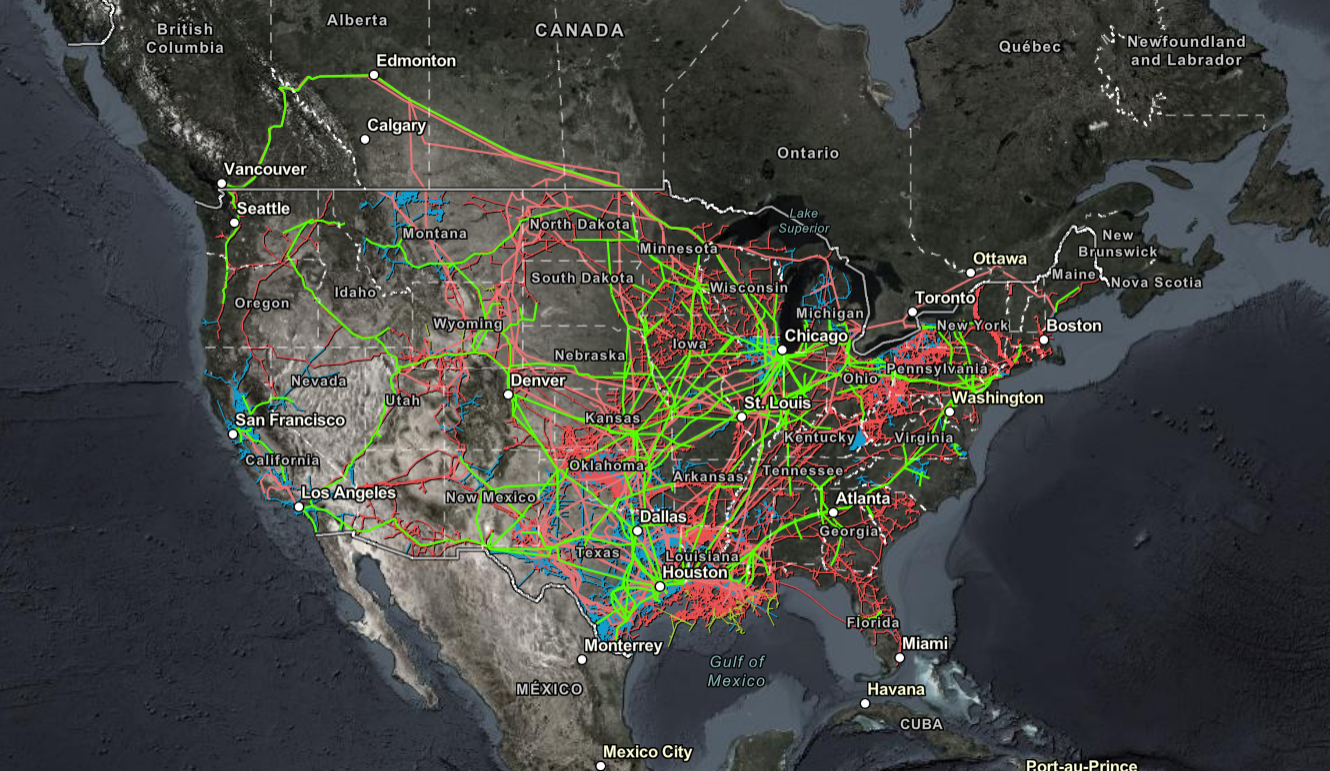
GIS Web Map Example: Pipelines

Online Live Mapping

Laser Scanning & 3D Simulation
The Power of 3D Simulations
In 3D modeling, large data sets from laser scanning can quickly overwhelm most computers. To make this data manageable and useful, it must be converted into easy-to-handle formats, often through 3D simulations. At Landpoint, these models can be customized to your team's needs and embedded with valuable information to speed up projects.
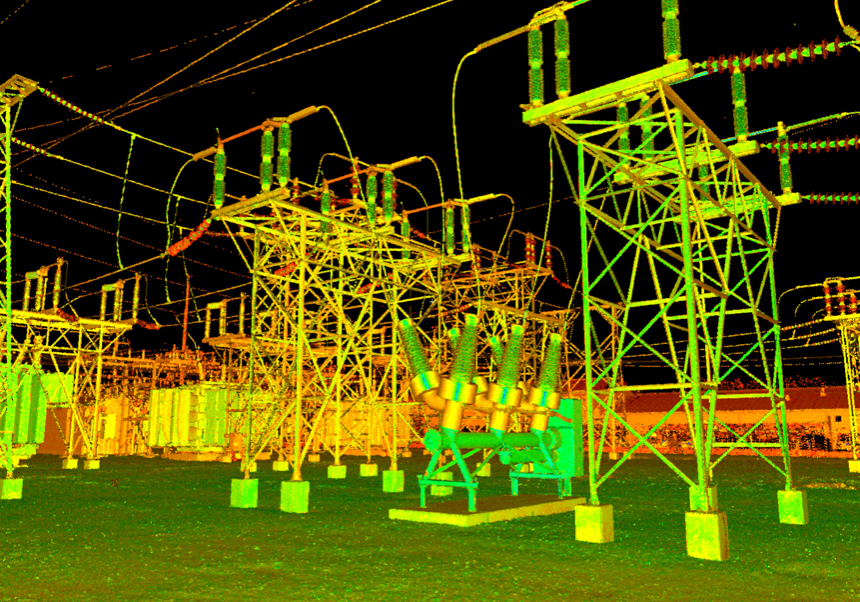

The Power of 3D Simulations
In 3D modeling, large data sets from laser scanning can quickly overwhelm most computers. To make this data manageable and useful, it must be converted into easy-to-handle formats, often through 3D simulations. At Landpoint, these models can be customized to your team's needs and embedded with valuable information to speed up projects.
StreamUp GPR
Subsurface Investigation
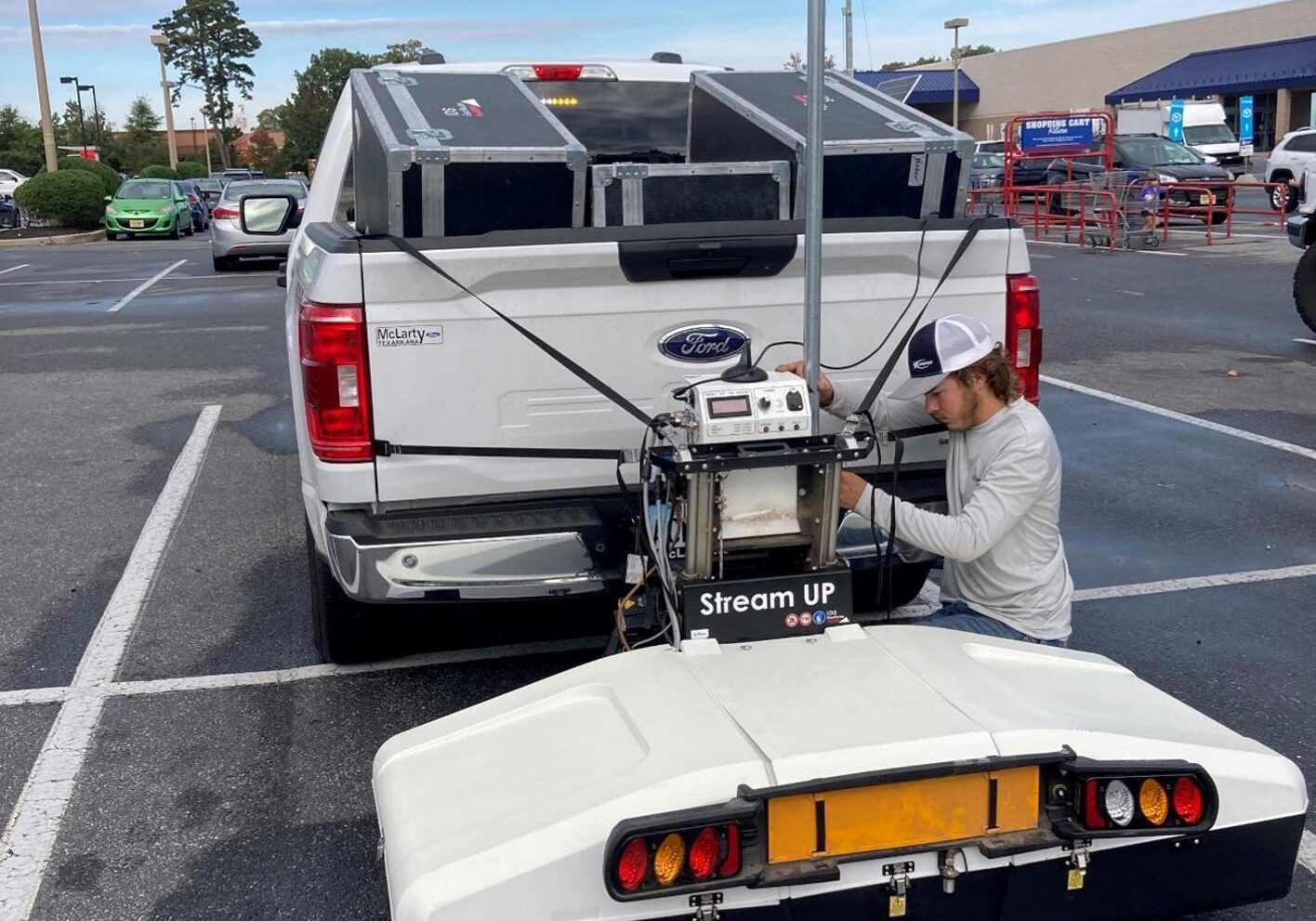

Subsurface Investigation
Quickview 360 Manhole Scanning
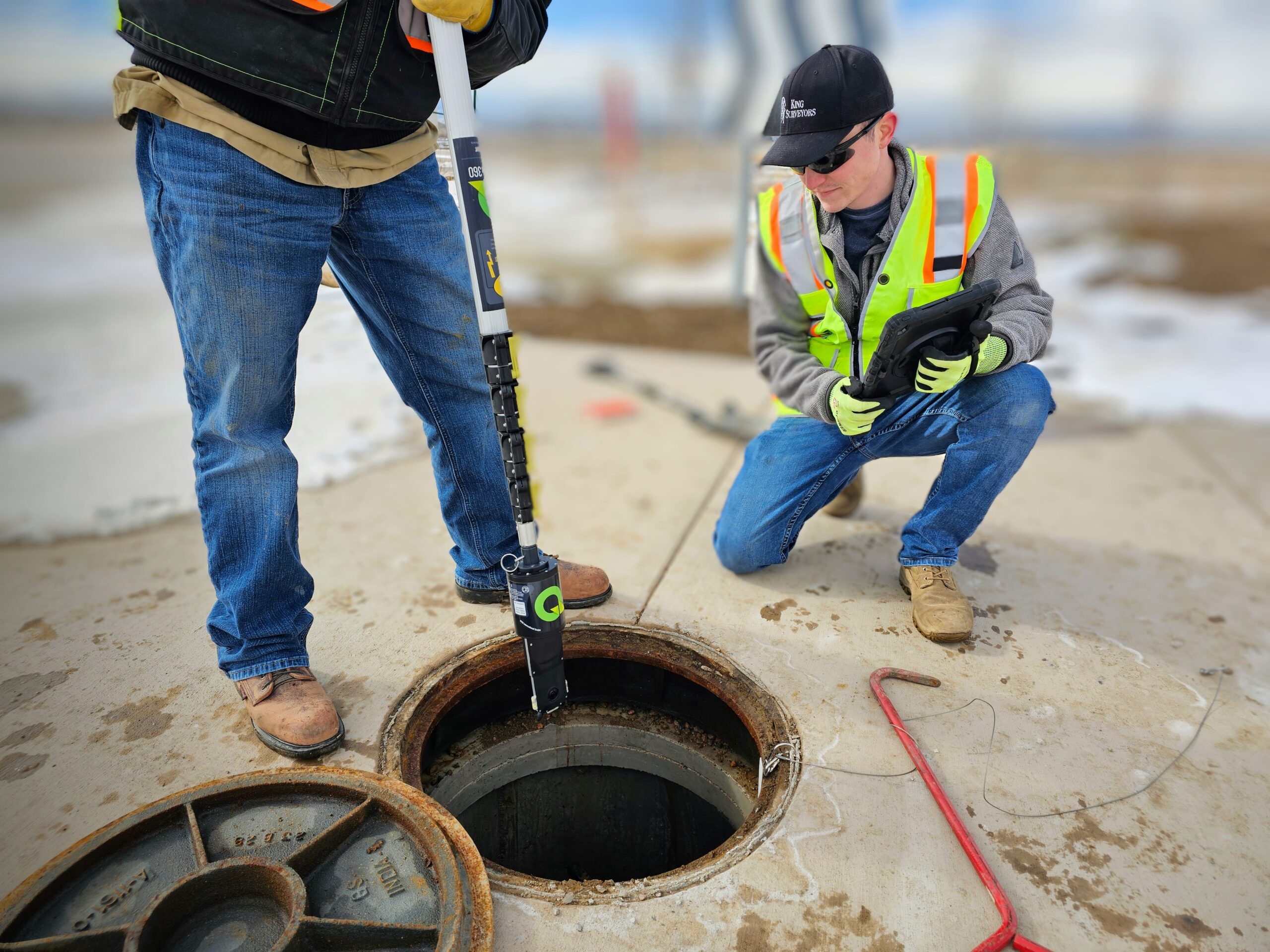

Manhole Inspections with Game Changing Technology
Transform your manhole inspections with Landpoint’s Quickview 360 HD Panoramic Video Service, a fast, affordable solution designed for maximum efficiency.
High-definition panoramic video is captured quickly and streamed securely to the cloud, where AI-powered tools assist with defect detection and feature coding.
Streamline reporting and perform in-depth analysis with access to a full 3D model for precise measurements, annotations, and seamless CAD exports.
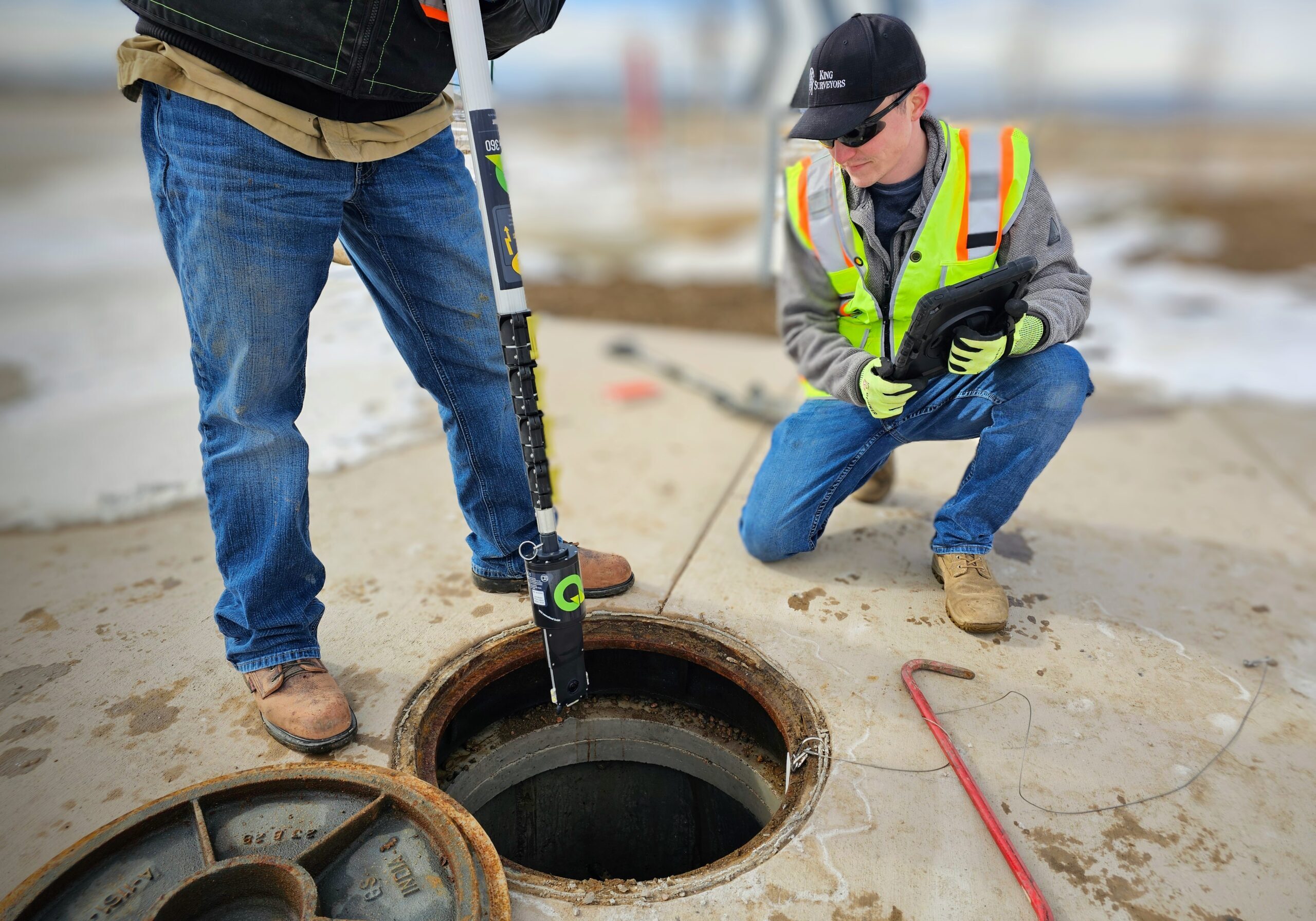

Manhole Inspections with Game Changing Technology
Transform your manhole inspections with Landpoint’s Quickview 360 HD Panoramic Video Service, a fast, affordable solution designed for maximum efficiency.
High-definition panoramic video is captured quickly and streamed securely to the cloud, where AI-powered tools assist with defect detection and feature coding.
Streamline reporting and perform in-depth analysis with access to a full 3D model for precise measurements, annotations, and seamless CAD exports.
Safety Is Our Priority
Safety is paramount in land surveying due to the inherent risks associated with working in diverse and sometimes hazardous environments. Landpoint, LLC takes great pride in our company’s safety culture, reflected in our overall statistical successes. We firmly believe that all work can be completed with the highest safety and quality. Surveyors are trained to adhere to strict safety protocols and use personal protective equipment (PPE) to mitigate these risks. Implementing safety management systems, utilizing technology, and adhering to industry best practices all reduce risks and promote a safe working environment for land surveyors.
